3 min read
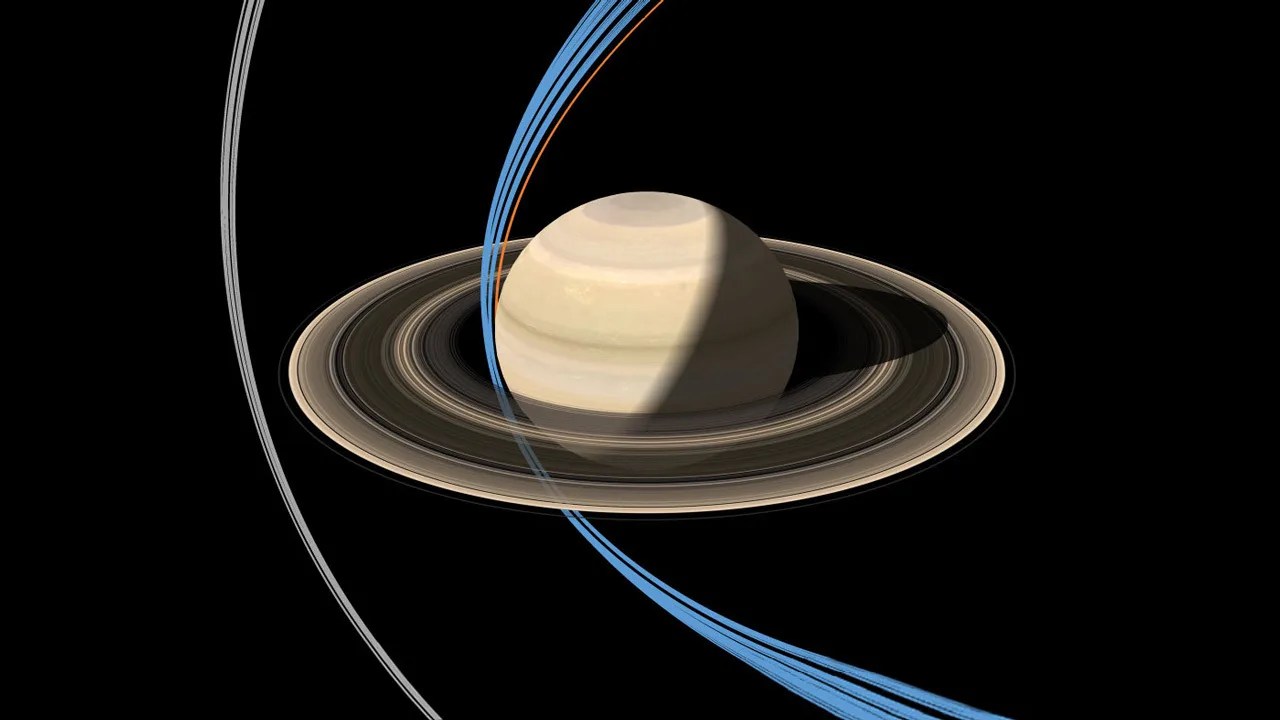

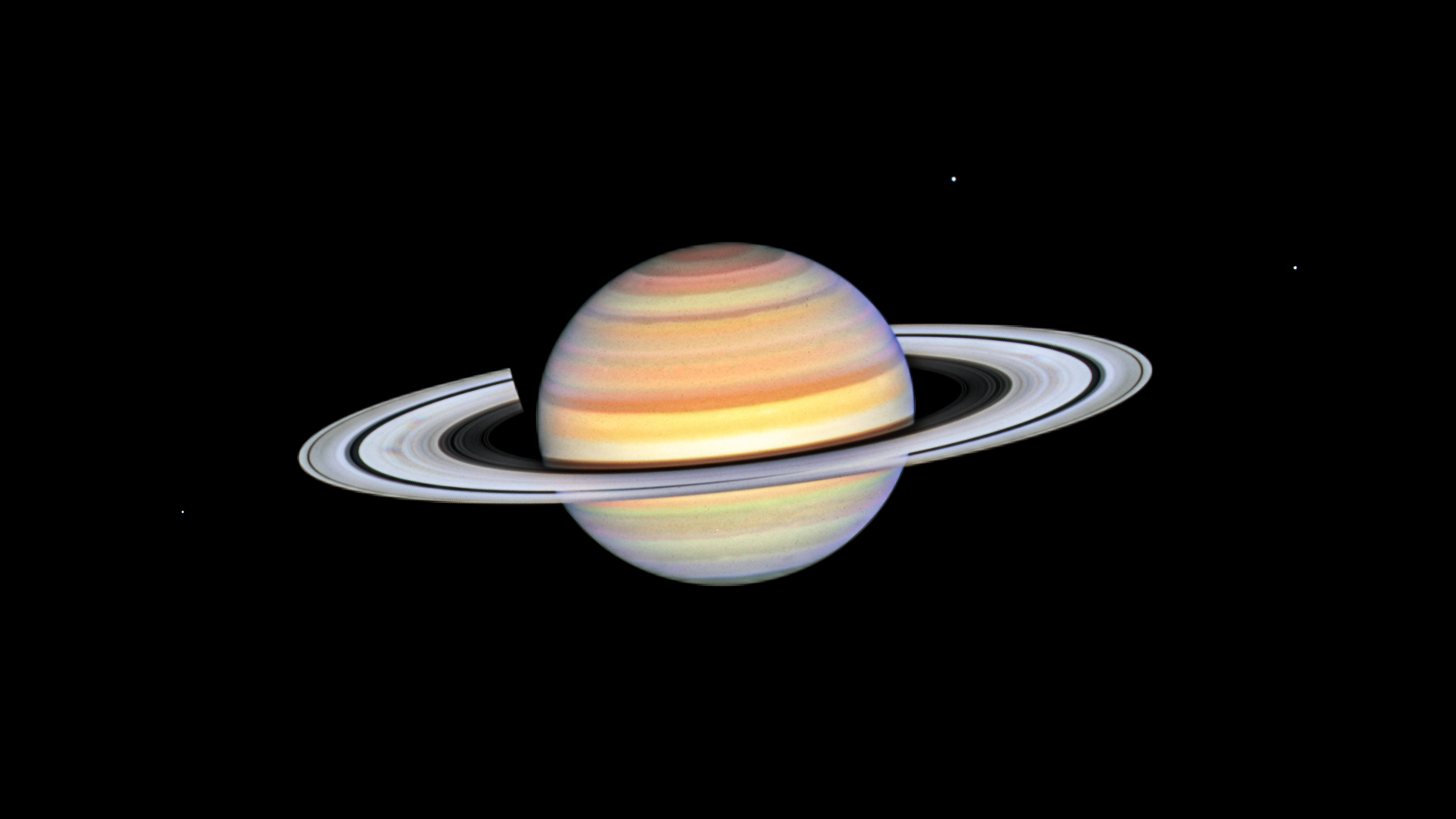
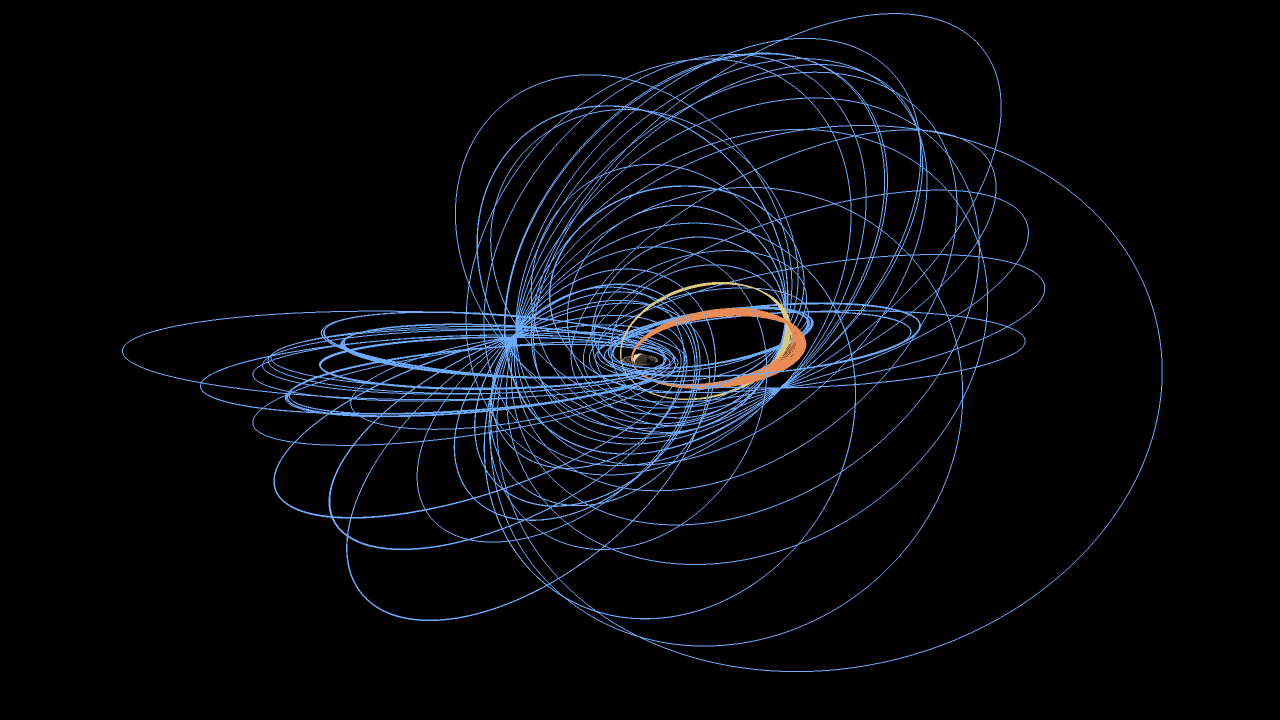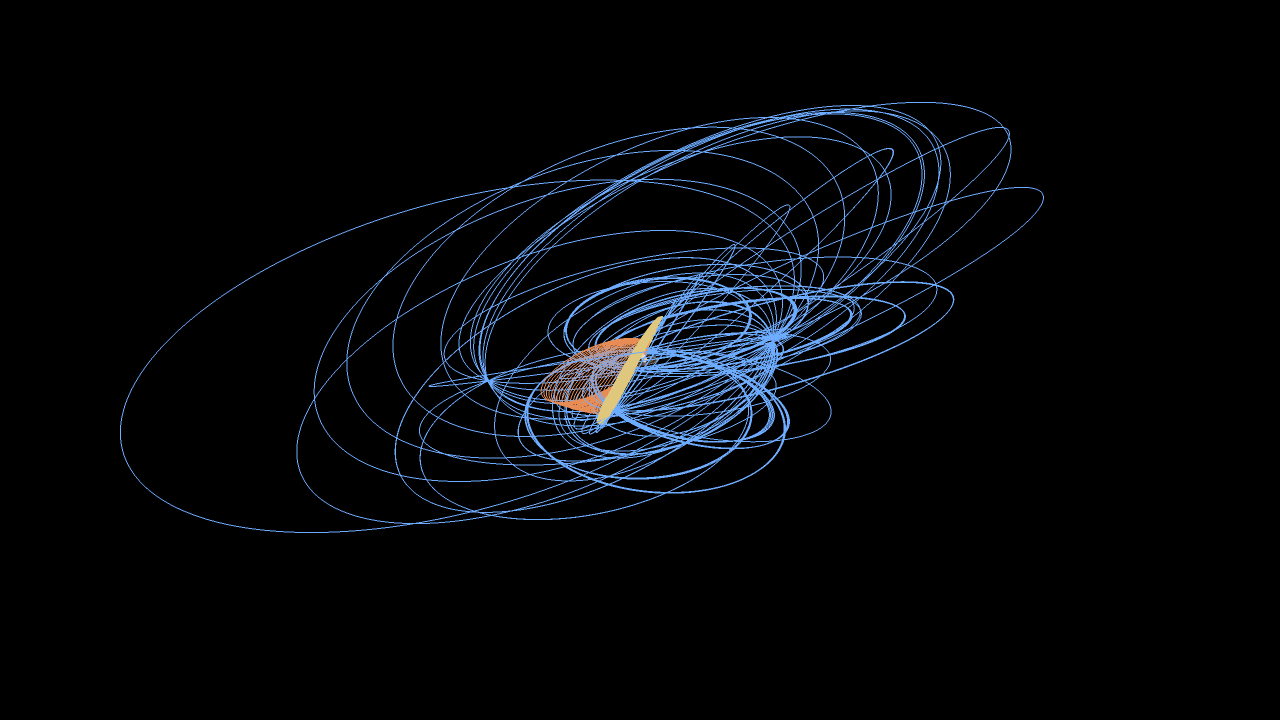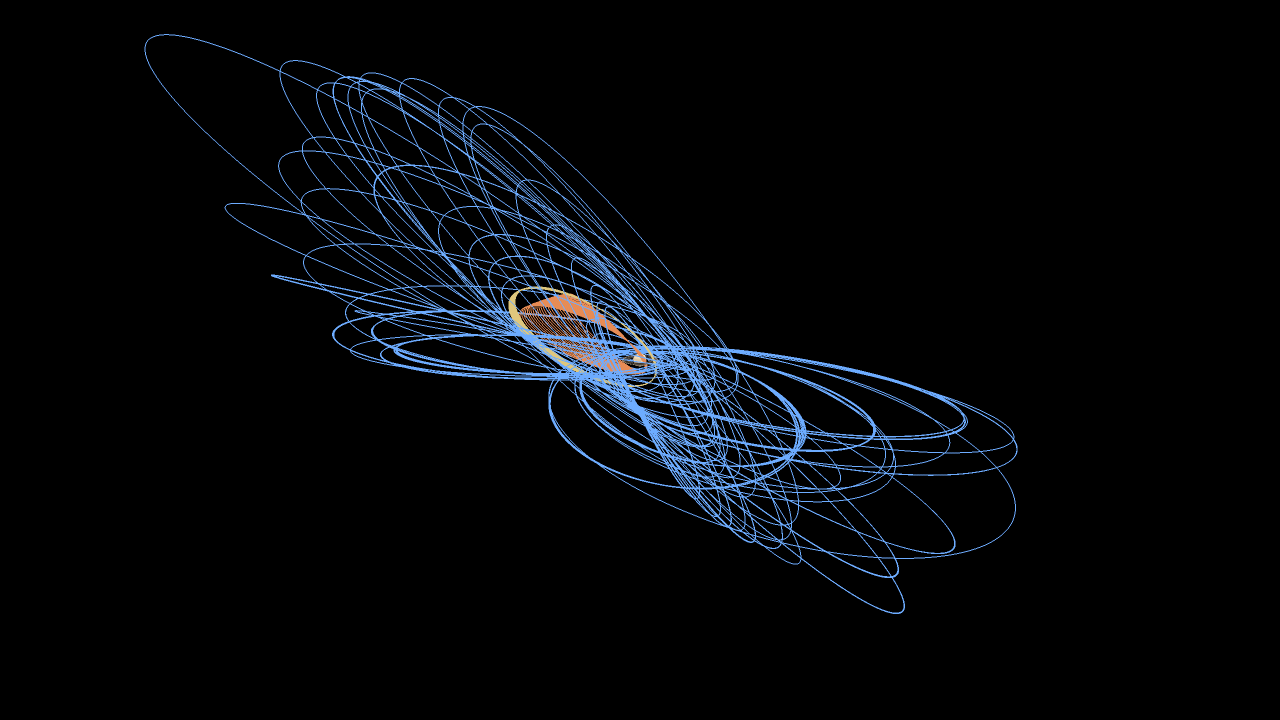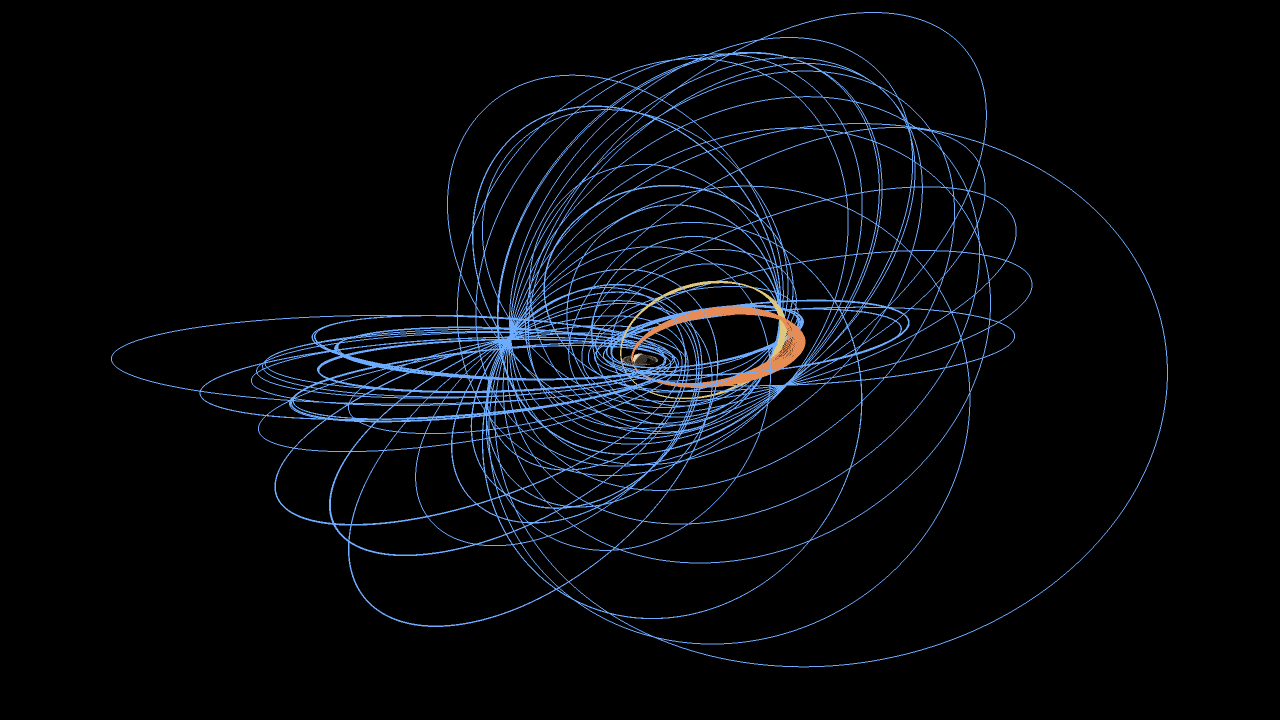
NASA's Saturn-orbiting Cassini spacecraft has made its first close dive past the outer edges of Saturn's rings since beginning its penultimate mission phase on Nov. 30.
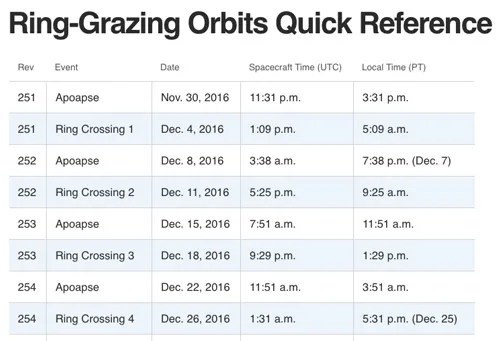
Cassini crossed through the plane of Saturn's rings on Dec. 4 at 5:09 a.m. PST (8:09 a.m. EST) at a distance of approximately 57,000 miles (91,000 kilometers) above Saturn's cloud tops. This is the approximate location of a faint, dusty ring produced by the planet’s small moons Janus and Epimetheus, and just 6,800 miles (11,000 kilometers) from the center of Saturn's F ring.
About an hour prior to the ring-plane crossing, the spacecraft performed a short burn of its main engine that lasted about six seconds. About 30 minutes later, as it approached the ring plane, Cassini closed its canopy-like engine cover as a protective measure.
"With this small adjustment to the spacecraft's trajectory, we're in excellent shape to make the most of this new phase of the mission," said Earl Maize, Cassini project manager at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California.
A few hours after the ring-plane crossing, Cassini began a complete scan across the rings with its radio science experiment to study their structure in great detail.
"It's taken years of planning, but now that we're finally here, the whole Cassini team is excited to begin studying the data that come from these ring-grazing orbits," said Linda Spilker, Cassini project scientist at JPL. "This is a remarkable time in what's already been a thrilling journey."
Cassini's imaging cameras obtained views of Saturn about two days before crossing through the ring plane, but not near the time of closest approach. The focus of this first close pass was the engine maneuver and observations by Cassini's other science instruments. Future dives past the rings will feature some of the mission's best views of the outer regions of the rings and small, nearby moons.
Each of Cassini's orbits for the remainder of the mission will last one week. The next pass by the rings' outer edges is planned for Dec. 11. The ring-grazing orbits -- 20 in all -- will continue until April 22, when the last close flyby of Saturn's moon Titan will reshape Cassini's flight path. With that encounter, Cassini will leap over the rings, making the first of 22 plunges through the 1,500-mile-wide (2,400-kilometer) gap between Saturn and its innermost ring on April 26.
On Sept. 15, the mission will conclude with a final plunge into Saturn's atmosphere. During the plunge, Cassini will transmit data on the atmosphere's composition until its signal is lost.
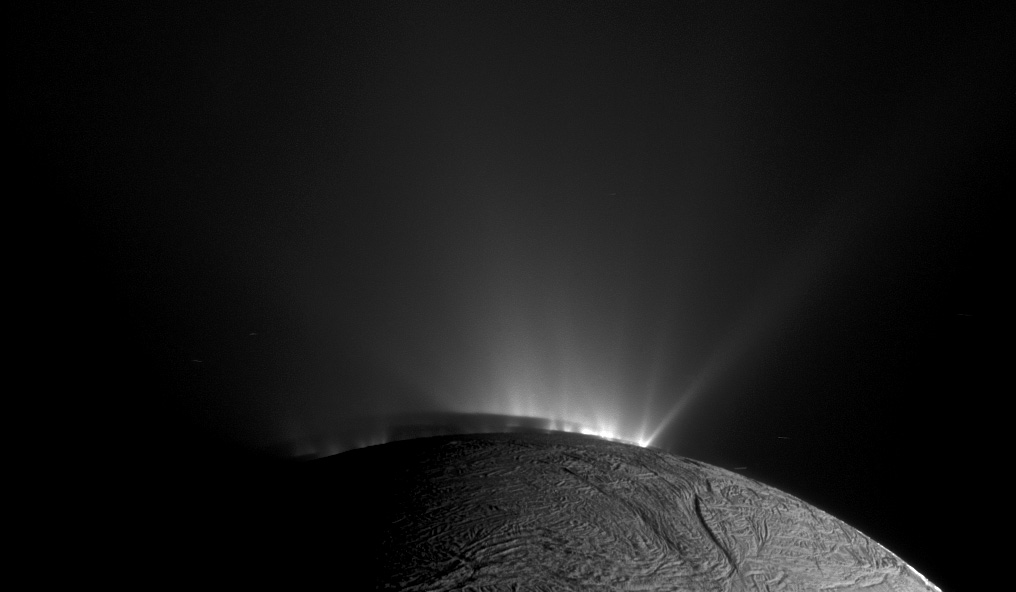
Launched in 1997, Cassini has been touring the Saturn system since arriving there in 2004 for an up-close study of the planet, its rings and moons. During its journey, Cassini has made numerous dramatic discoveries, including a global ocean with indications of hydrothermal activity within the moon Enceladus, and liquid methane seas on another moon, Titan.
For details about Cassini's ring-grazing orbits, visit:
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed, developed and assembled the Cassini orbiter.
More information about Cassini is at:
Preston Dyches
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-7013
preston.dyches@jpl.nasa.gov